Anticholesterol drug is also known as HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, are a class of lipid-lowering medications. Statins have been found to reduce cardiovascular disease (CVD) and mortality in those who are at high risk of cardiovascular disease. The evidence is strong that statins are effective for treating CVD in the early stages of the disease (secondary prevention) and in those at elevated risk but without CVD (primary prevention)
The statins are divided into two groups: fermentation-derived and synthetic. They include, along with brand names, which may vary between countries:
| Statin | Image | Brand name | Derivation | Metabolism |
|---|---|---|---|---|
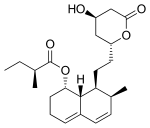
| Atorvastatin | Lipitor, Ator | Synthetic | CYP3A4 | |
| Cerivastatin | Lipobay, Baycol (withdrawn from the market in August, 2001 due to risk of serious rhabdomyolysis) | Synthetic | various CYP3Aisoforms | |
| Fluvastatin | Lescol, Lescol XL | Synthetic | CYP2C9 | |
| Lovastatin | Mevacor, Altocor, Altoprev | Naturally occurring, fermentation-derived compound. It is found in oyster mushroomsand red yeast rice | CYP3A4 | |
| Mevastatin | Compactin | Naturally occurring compound found in red yeast rice | CYP3A4 | |
| Pitavastatin | Livalo, Livazo, Pitava | Synthetic | CYP2C9 and CYP2C8(minimally) | |
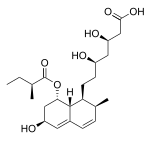
| Pravastatin | Pravachol, Selektine, Lipostat | Fermentation-derived (a fermentation product of bacterium Nocardia autotrophica) | Non-CYP | |
| Rosuvastatin | Crestor | Synthetic | CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 | |
| Simvastatin | Zocor, Lipex | Fermentation-derived (simvastatin is a synthetic derivate of a fermentation product of Aspergillus terreus) | CYP3A4 | |
| Simvastatin + ezetimibe | Vytorin, Inegy | Combination therapy: statin + cholesterol absorption inhibitor | ||
| Lovastatin + niacin extended-release | Advicor, Mevacor | Combination therapy | ||
| Atorvastatin + amlodipine | Caduet, Envacar | Combination therapy: statin + calcium antagonist | ||
| Simvastatin + niacin extended-release | Simcor | Combination therapy |
LDL-lowering potency varies between agents. Cerivastatin is the most potent, (withdrawn from the market in August 2001 due to the risk of serious rhabdomyolysis) followed by (in order of decreasing potency), rosuvastatin, atorvastatin, simvastatin, lovastatin, pravastatin, and fluvastatin. The relative potency of pitavastatin has not yet been fully established.
The oyster mushroom, a culinary mushroom, naturally contains lovastatin.
Some types of statins are naturally occurring and can be found in such foods as oyster mushrooms and red yeast rice. Randomized controlled trials have found these foodstuffs to reduce circulating cholesterol, but the quality of the trials has been judged to be low. Due to patent expiration, most of the block-buster branded statins have been generic since 2012, including atorvastatin, the largest-selling branded drug.
| Statin equivalent dosages | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % LDL reduction (approx.) | Atorvastatin | Fluvastatin | Lovastatin | Pravastatin | Rosuvastatin | Simvastatin |
| 10–20% | – | 20 mg | 10 mg | 10 mg | – | 5 mg |
| 20–30% | – | 40 mg | 20 mg | 20 mg | – | 10 mg |
| 30–40% | 10 mg | 80 mg | 40 mg | 40 mg | 5 mg | 20 mg |
| 40–45% | 20 mg | – | 80 mg | 80 mg | 5–10 mg | 40 mg |
| 46–50% | 40 mg | – | – | – | 10–20 mg | 80 mg* |
| 50–55% | 80 mg | – | – | – | 20 mg | – |
| 56–60% | – | – | – | – | 40 mg | – |
| * 80-mg dose no longer recommended due to increased risk of rhabdomyolysis | ||||||
| Starting dose | ||||||
| Starting dose | 10–20 mg | 20 mg | 10–20 mg | 40 mg | 10 mg; 5 mg if hypothyroid, >65 yo, Asian | 20 mg |
| If higher LDL reduction goal | 40 mg if >45% | 40 mg if >25% | 20 mg if >20% | — | 20 mg if LDL >190 mg/dL (4.87 mmol/L) | 40 mg if >45% |
| Optimal timing | Anytime | Evening | With evening meals | Anytime | Anytime |
Evening |
References

![]()




















About the author