Hyperthermia is elevated body temperature due to failed thermoregulation that occurs when a body produces or absorbs more heat than it dissipates. Extreme temperature elevation then becomes a medical emergency requiring immediate treatment to prevent disability or death.
Normal Temperature of the Human Body
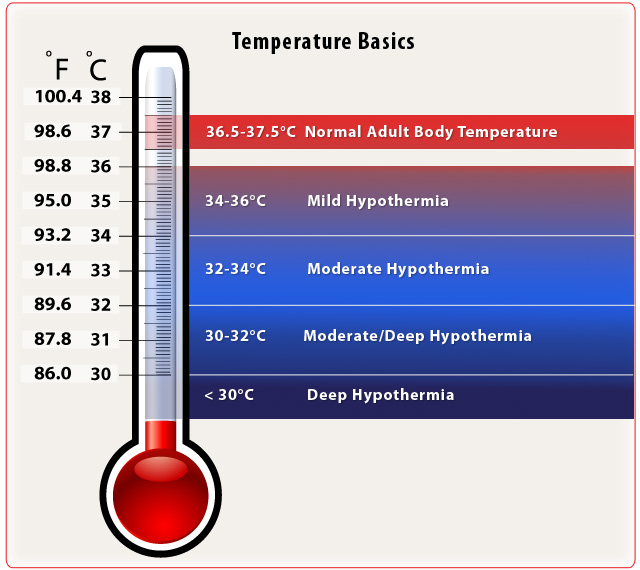
- The normal body temperature of humans ranges from 36.5 to 37.5 degrees Celsius.
- However, during late afternoons, when the atmospheric temperature is at its peak, the normal body temperature can still reach to as high as 37.7 degrees Celsius. Temperatures recorded below and above these levels are considered to be the conditions hypothermia and hyperthermia, respectively. Consequently, any abnormality in body temperature can lead to experiencing medical problems.
Neutral thermal environment (NTE) – narrow range of environmental temperature in which a person is able to maintain a neutral thermal temperature. A neutral thermal temperature is the body temperature at which an individual’s oxygen and energy consumption is minimised.
Fever
- pertaining to or marked by a fever
- is caused by a change in the body’s temperature set point, usually caused by infection
Temperature 37.2 – 38.0°C –
Temperature > 38.0° C-
Hypothermia: Body’s core temperature drops below that required for normal metabolism and body functions Neonate- a temperature <36.5 ºC
Infant/child- a temperature <36 ºC
www.rxharun.com
Hyperthermia – Is an elevated body temperature due to failed thermoregulation that occurs when the body produces or absorbs more heat than it can dissipate. Hyperthermia differs from fever in the mechanism that causes the elevated body temperature.
Mild hyperthermia -a temperature>37.5 ºC
Extreme hyperthermia – a temperature > 38.8 ºC
Heat Stroke – Thermoregulation is overwhelmed by a combination of excessive metabolic production of heat (exertion), excessive environmental heat and insufficient or impaired heat loss. This results in an abnormally high body temperature
Neonate – an infant that is up to 28 days corrected post term (e.g. an infant born at 34 weeks gestation and is 8 weeks old is 14 days corrected post term).
Non shivering thermogenesis – The primary source of heat production in the neonate. It is the production of heat by metabolism of brown fat Brown fat (deposited after 28 weeks gestation principally around the scapulae, kidneys, adrenals, neck and axilla) is a thermogenic organ unique neonates.
Methods of heat loss
- Conduction – Transfer of heat from one solid object to another solid object in direct contact with it
- Convection – Transfer of heat from the body surface to the surrounding air via air current
- Radiation –Transfer of heat to cooler solid objects not in direct contact with the body
- Evaporation – Heat loss occurring during conversion of liquid to vapour
Radiant warmer
Radiant warming cots are designed to provide thermal stability to infants while allowing direct observation. These cots can be operated in servo control mode (the heating elements turn on and off according to measured changes in the infant’s skin temperature) or manual control (the heater is set to a constant power level).
Isolette – The trademark name for an autonomous incubator unit that provides a controlled heat, humidity and oxygen microenvironment for the isolation and care of premature and low birth weight neonates, and infants. The device is made of a clear plastic material and has a large door and smaller portholes for easy access to the infant with a minimum of heat and oxygen loss. A servo control mechanism can be used to constantly monitor the infant’s temperature and control the heat within the unit.
There are two main causes of heat stroke:
- Exertional heat stroke – occurs when someone is vigorously active in a hot environment, such as playing sports on a hot summer day or participating in military training activities. It typically strikes young, otherwise healthy people, those least likely to be concerned about the effects of heat on their health. Because of the lack of concern, early symptoms may be dismissed or ignored.
- Nonexertional heat stroke – tends to occur in people who have a diminished ability to regulate body temperature, such as older people, very young children or people with chronic illnesses. High heat in the surrounding environment, without vigorous activity, can be enough to cause heat stroke in these people.
Furthers Categories of Heat Illness
Minor Heat Illness
- Heat Cramps: Intermittent muscle cramps likely related to salt deficiency
- Heat Edema: Swelling of the feet and ankles typically in non-acclimatized people
- Heat Syncope: Caused by peripheral vasodilation of decrease venous return
- Prickly Heat: Vesicular rash caused by obstruction of the sweat gland pores
Heat Exhaustion
- Moderate temperature Elevation (typically < 40oC)
- Caused by volume depletion secondary to heat stress
- Variant forms: water depletion, salt depletion
- Symptoms + Signs
- Nonspecific symptoms: Weakness, fatigue, headache, nausea/vomiting, muscle cramps
- Syncope
- Orthostatic hypotension
- Continued sweating
- Intact neurologic function
Management
- Serum electrolyte measurement to help guide fluid management
- Symptomatic management
Heat Stroke
Physiologic Changes in Heat Stroke
- Cardiovascular
- Hypodynamic states seen in elderly (or those with compromised cardiac function at baseline)
- Hyperdynamic states in young patients
- Mild volume depletion
- Edema and hemorrhage in the GI tract occur (likely due to regional ischemia)
- Acute kidney injury (AKI)
- Contributors: volume depletion, hypotension, myoglobinuria
- Coagulopathy
- Electrolyte disturbances: hypernatremia, hyperkalemia, hypophasphatemia, hypocalcemia
Clinical Manifestations , Vital Sign Abnormalities
- Hyperthermia (typically > 41oC)
- Tachypnea
- Tachycardia
- Hypotension
- Hot, dry skin with absence of sweating
- CNS dysfunction: altered mental status, seizures, com
- Heat exhaustion is a warning that your body can no longer keep itself cool. You might feel thirsty, dizzy, weak, uncoordinated, and nauseated. You may sweat a lot. Your body temperature may stay normal, but your skin may feel cold and clammy. Some people with heat exhaustion have a rapid pulse. Rest in a cool place and get plenty of fluids. If you don’t feel better soon, get medical care. Be careful—heat exhaustion can progress to heat stroke
Causes of Hyperthermia
A number of factors can increase one’s chances of acquiring hyperthermia, this includes:
- Previous history of heat-related disease
- Age extremes (very young, very old)
- Heat intolerance due to poor acclimatization to the environment (such as a heavy coated dog in a hot geographical location)
- Obesity
- Poor heart/lung conditioning
- Underlying heart/lung disease
- Increased levels of thyroid hormone (hyperthyroidism)
- Short-nosed, flat-faced (brachycephalic) breeds
- Thick hair coat
- Dehydration, insufficient water intake, restricted access to water.
- Being out and exposed in direct heat for a long period of time
- In close distance to a heat-inducing equipment for an extensive amount of time
- Inability to rehydrate
- Inability to seek and relocate to an area with a greater amount of shade and a lesser degree of temperature level
- Included in the younger age group
- Increased poverty
- Engaging in outdoor daytime activities for a lengthy period of time
- Certain medical disorders including pheochromocytoma, thyrotoxicosis, status epilepticus and brain hemorrhage.
- Having heat exhaustion and heat strokes, which are comprised of too much metabolic heat production, excessive environmental heat, and nonfunctioning heat losing mechanism
- Intake of medications such as monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and tricyclic antidepressants
Factors that can contribute to heat stroke/hyperthermia include:
- Dehydration from not drinking enough water
- Wearing bulky or heavy clothing, such as firefighting gear, in the heat
- Being overweight, which causes the body to generate more heat and reduces the body’s ability to cool down
- Sleep deprivation, which can decrease the rate of sweating
- Being unaccustomed to the heat, such as moving from a cooler climate to a warmer climate
- Some medications, most commonly antihistamines (taken for allergies), diuretics (taken for high blood pressure or leg swelling), laxatives (taken to relieve constipation), calcium channel blockers (one type of blood pressure or heart medicine), medicines for Parkinson’s disease, some diarrhea treatments and tricyclic antidepressants
- Being confined to a poorly ventilated or non-air-conditioned living space
- Having had heat stroke in the past
- Use of illicit drugs, including cocaine, heroin, amphetamines and ecstasy (MDMA)
Symptoms of Hyperthermia
Hyperthermia can be categorized as either fever or non-fever hyperthermias; heat stroke is a common form of the latter. Symptoms of both types include:
- Abdominal cramps
- Muscle cramps
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Weakness
- Dehydration/heavy sweat or a lack of sweat
- Excessive drooling (ptyalism)
- Increased body temperature – above 103° F (39° C)
- Reddened gums and moist tissues of the body
- Production of only small amounts of urine or no urine
- Sudden (acute) kidney failure
- Rapid heart rate
- Irregular heart beats
- Shock
- Stoppage of the heart and breathing (cardiopulmonary arrest)Fluid build-up in the lungs; sudden breathing distress (tachipnea
- Blood-clotting disorder(s)
- Vomiting blood (heamatosis)
- Passage of blood in the bowel movement or stool
- Black, tarry stools
- Small, pinpoint areas of bleeding
- Generalized (systemic) inflammatory response syndrome
- Disease characterized by the breakdown of red-muscle tissue
- Death of liver cells
- Changes in mental status
- Seizures
- Muscle tremors
- Wobbly, incoordinated or drunken gait or movement (ataxia)
- Unconsciousness in which the dog cannot be stimulated to be awakened
When heat stroke starts, neurological symptoms can include:
- Odd or bizarre behavior
- Irritability
- Delusions
- Hallucinations
- Seizures
- Coma
Symptoms and signs of malignant hyperthermia include:
- A dramatic rise in body temperature, sometimes as high as 113 degrees Fahrenheit
- Rigid or painful muscles, especially in the jaw.
- Flushed skin
- Sweating
- An abnormally rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Rapid breathing or uncomfortable breathing
- Brown or cola-colored urine
- Very low blood pressure (shock)
- Confusion
- Muscle weakness or swelling after the event
Many people who carry a gene for malignant hyperthermia will never develop symptoms.
Diagnosis of hyperthermia
Serum labs
Basic metabolic panel
- Common electrolyte abnormalities (hypoNa, hypoK, hypo Ca, hypophosphatemia)
- Acute kidney injury
Hepatic panel
- ALT/AST rise + peak within 48 hours
- Fulminant hepatic failure may be seen
Cardiac biomarkers
- Troponin often elevated but may be unclear if type I (coronary occlusion) or type II ischemia
Creatine kinase (CK)
- Muscle breakdown common in younger patients resulting from physical activity or agitation
- CK levels do not correlate with severity of rhabdomyolysis or AKI
- Can reveal rhabdomyolysis (+ blood with minimal or no RBCs on micro)
- Can reveal concomitant urinary infection
EKG
- Nonspecific ST and T wave changes are common
- Ventricular tachydysrhythmias (VF + VT) can occur
Differentiating sepsis from heat stroke can be difficult
- unless there is a clear exposure history (i.e. sports related). Additionally, patients can have both infection and heat stroke concomitantly. It is not unreasonable to administer broad spectrum antibiotics if there is a suspicion for an infectious process.
Treatment of hyperthermia
Basic Interventions
- Large bore IV access X 2, supplemental oxygen (pre-oxygenation for possible RSI), cardiac monitor
- Consider early airway management for altered mental status or seizure activity
- Continuous core temperature monitoring (i.e. rectal or esophageal probe, bladder probe)
- Finger stick glucose
- There is no role for the use of antipyretics in hyperthermia management (hypothalamic thermoregulation is not affected)
- Aggressive external cooling measures
- Patients should be rapidly cooled (< 30 min) to a target temperature of 38.3oC (101oF)
- Ice bath immersion is superior to other forms of cooling
- Remove from ice bath at 38.3oC to prevent iatrogenic hypothermia
- Delays in cooling are associated with high morbidity and mortality
- Patients should be rapidly cooled (< 30 min) to a target temperature of 38.3oC (101oF)
- Treat agitation and shivering with benzodiazepines to prevent excess heat generation
As soon as malignant hyperthermia is suspected, doctors must act rapidly to treat the condition and prevent complications.
The first and most important step is to immediately stop giving the triggering medication and to stop the surgery. Doctors then give the drug dantrolene (Dantrium).
Dantrolene relaxes the muscles. It stops the dangerous increase in muscle metabolism.
Dantrolene is given intravenously until a patient has stabilized. Then, the medication typically is continued in pill form for three days.
Additional treatment can include:
- Lowering body temperature with:
- Cool mist and fans
- Cooling blankets
- Cooled intravenous fluids
- Administering oxygen
- Using medications to:
- Control the heartbeat
- Stabilize blood pressure
- Monitoring in an intensive care unit
Most cases of heat stroke can be prevented. When the temperature outside is especially high:
- Drink lots of water throughout the day.
- Stay indoors in an air-conditioned area whenever you feel too warm.
- Wear lightweight, light-colored clothing, preferably with a loose-weave material that lets air get to your skin.
- Avoid strenuous activity in the hottest part of the day (between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.). If you must participate, take frequent breaks, limit the time that you wear a helmet by taking it off between activities, and avoid wearing heavy uniforms or equipment.
- Drink less caffeine and alcohol, which can contribute to dehydration.
If you begin to feel tired, dizzy or nauseated, or if you develop a headache, get out of the heat immediately. Seek out an air-conditioned building. Drink water. If possible, take a cool shower or bath or use a hose to soak yourself.
Home Remedies for hyperthermia
1. Cold Coffee
Even there are many different beverages considered as home remedies to reduce body heat that could help a lot in keeping the body cool on hot summer days. For instance, cold coffee could be an ideal way to keep the body cool in low temperature. Certainly, adding ice to your coffee could help you retain the normal level of body heat on hot weather days. People can also use the shaker to make the drink more delicious and colder.
Cold Milk
Keep raw milk in your fridge and consume it on a regular basis to reduce your body temperature as well as the heat inside your entire system. This is actually one of the best home remedies to reduce body heat that everyone should try and make use right from today for good! Ensure that your milk would be not too cold. You could also create your own milkshake out of it by adding to the milk with the flavors you personally like.
Splash Of Water
In fact, water is among the most basic and useful home remedies to reduce body heat on hot summer days. You just need to consume proper amounts of water every single day for washing away the heat produced inside the whole body. In addition, the oxidants presented inside your body also contribute to the increased heat inside the human body.
Apricot
Consume a glass of honey mixed with apricot juice to cool down the heat inside the body and quench your thirst as the effective home remedies to reduce body heat. Since apricots are available in the hard form, people have to extract the juice out of them. Once you get the apricot juice extracted, you could simply consume it without needing to think twice.
Peaches
Excess body temperature can affect skin negatively and often end in skin soreness as well as rashes. Peach is generally well-known as an excellent source of potassium, vitamin A new, and the rich vitamin B2 content, which are essential for people to maintain healthy body and skin. Dried peach can also aid a lot in regulating the levels of heat produced inside our body as home remedies to reduce body heat.
Vitamin C Rich Vegetables
Veggies that are abundant in vitamin C and also citrus fruits such as sweet lemon and orange are wonderful food items considering as home remedies to reduce body heat that can help a lot in relieving the body temperature. During hot weather days when the body gets heat up both from external and internal ways, eating veggies and fruits that are rich in vitamin C can help a lot in decreasing the excess body heat problem. People can also try drinking some vitamin C – rich juices, such as lemon juice and orange juice.
Home Remedies To Reduce Body Heat – Honey And Milk
If you are looking for the ideal drinks and foods to control the body temperature within hot weather days, then a perfect mixture of cold milk and honey would do you a favor. There is also a special preparation way for this remedy. Everything we need to do is just to add 1 tbsp. of honey in a sufficient amount of cold milk and consume the mixture every day for quick and good results.
Home Remedies To Reduce Body Heat – Bananas
This wonderful fruit is not just rich in essential nutrients but also provides great cooling effects. The potassium content of banana offers a great cooling effect on human body. It can also aid a lot in digesting spicy and heavy foods. You should consume 1 banana after having any meal throughout the day as a light desert to digest foods faster and cool down your body heat naturally.
Sugarcane
The juice extracted from sugarcane is the favorite juice of many people out there. With a high level of sugar content, it can help to boost the energy levels inside your entire body. In addition, sugarcane juice has an amazing cooling effect that can help to cool down the whole temperature of the body. Consuming one glass of sugarcane juice on a daily basis can help a lot in balancing the body heat in hot summer days.
Pomegranate
Pomegranate could be considered as a heavenly fruit because of its rich contents of essential vitamins and minerals. Patients with cancers and other fatal diseases undergoing medical treatments are recommended to consume pomegranate juice every day because it can help to recover the body within a very short time period.
You could also drink a glass of fresh pomegranate juice in a mixture with 2 – 3 drops of almond oil on a daily basis, in the morning of course.
Fennel Seed
This Indian spice is famous all over the world for its flavor and aroma. It provides several health advantages. One of such health benefits is to cool down the body temperature. Try soaking fennel seeds and let them stay overnight. Strain the solution the next morning and consume it.
Radish
Many people do not like radish because of its taste. However, why don’t you eat it in summer as it is very good for reducing body heat? Being very abundant in water, radish, considered one of home remedies to reduce body heat, that can help to cool down the body effectively. It is also an excellent source of antioxidants and vitamin C. During hot weather days, heat stroke is quite common among us.
Cucumber
Cucumber is one of the healthy foods that are most widely eaten in India during summer days. Thanks to the cooling effects it provides that can instantly act to cool down body heat. Cucumber is very tasty and watery that everyone likes it. Consume more of this veggie by adding it to your salads on a daily basis to beat off heat stress.
Honeydew Melon
This is another contender coming from the family of melons that can help to lower body temperature. Add honeydew melon into your daily meals during hot weather days as one kind of home remedies to reduce body heat.
Muskmelon
All members of the melon family offer the cooling property to the human body. Muskmelon is also a fruit that is very rich in water and loaded with essential nutrients for preventing heat stress. Consume muskmelon juice on a daily basis to fight against health problems related to body heat.
Cardamom
Cardamom (well-known as elaichi) is an Indian spice that is used widely for cooking dishes. Cardamom has great detoxifying properties which thereby can help to reduce body heat as well. Cardamom could go with the tea form and you can consume it with ease.
Cool Water
Cool water is one of the best home remedies to reduce body heat effectively. In addition, it also helps your body recover fast from the side effects of high temperature. For optimal results, you can use it as follows.
- When your temperature increases, you should enjoy a tall glass of cool water. Afterward, you sip some cool water every 20 minutes.
- Another option is to take ice cubes to a foot tub and then fill it with cool water. Soak your feet in the bucket for about 15 to 20 minutes.
- The other way is to enjoy a cool bath to decrease body heat.
Coconut Water
Coconut water is also considered as one of the effective home remedies to reduce body heat. Its electrolyte composition is very effective for rehydrating your body. In addition, it is loaded with nutrients that will help lift your energy. Simply, you need only drink one glass of tender coconut water several times daily for best results.
Lemon
Using lemon regularly can prevent heat-related illnesses as well as keep the body cool. The high vitamin C presents in lemon can help reduce body temperature. In addition, it also oxygenates and hydrates the body to maintain you feeling refreshed and energized during the hot summer days. For positive effects, you should use it as follows.
- Squeeze the juice from about ½ lemon into water (a glass).
- Then add honey (1 teaspoon) and a pinch of salt to it.
It is recommended to enjoy about 3 glasses of lemon juice per day as one of home remedies to reduce body heat.
Sandalwood
Sandalwood is also one of the great home remedies to reduce body heat due to its soothing and cooling properties. It is used to decrease body heat as follows.
- Mix sandalwood powder (2 tablespoons) with enough cold milk or water to create a fine paste. Then add rose water (a few drops) and next to rub this paste on your chest and forehead. Let it to dry on its own and then wash it off with lukewarm water.
- Another method is to rub a little sandalwood oil on your forehead and then leave it on for some hours. You should add sandalwood oil (a few drops) in coconut oil (one teaspoon) and then apply to avoid skin irritation.
- The other option is to sprinkle sandalwood powder on your chest, back and armpits after taking a shower in order to keep cooler body temperature.
Peppermint
Peppermint also contains a cooling and soothing effect. Therefore, it is also one of the effective home remedies to reduce body heat. In addition to reducing body heat, it also helps to reduce headaches and relieve nausea as well. To see instant results, you should use it as following options.
- Simmer fresh peppermint leaves (a few ounces) in one pot of boiling water for at least 15 minutes. Next to strain out these leaves and then let the water cool down. After that, you add this peppermint-infused water to a bathtub filled with the cool bath water and immerse in it for at least 25 minutes. Another way is to prepare a peppermint bath by adding peppermint essential oil (a few drops) to cool bath water.
- Another option is to steep dried or fresh peppermint leaves (one teaspoon) in a cup of hot water.
Watermelon
Watermelon can help in reducing body heat quickly thanks to its high water content. Especially, eating watermelon regularly will also help keep you hydrated. For desirable results, you can use it to reduce body heat as follows.
- Eat watermelon (a few slices), or combine it with some sugar and cold milk to make a refreshing drink.
- Another choice among home remedies to reduce body heat is to mix cubes of watermelon with muskmelon and cucumber. Then add a little balsamic vinegar and olive oil over it in order to make a healthy salad.
Aloe Vera
Aloe vera is one of the most popular home remedies to reduce body heat. Its cooling and soothing properties can help keep normal body temperature. For positive result, aloe vera is used as follows.
- You can take fresh aloe vera gel and then apply it over your body. Allow it on for at least 20 minutes and then take a cold bath. You can repeat as needed.
- Another way is to drink homemade aloe vera juice (a glass) prepared with up to aloe vera gel (2 tablespoons). You should not drink more than two tablespoons of aloe vera gel per day.
Indian Gooseberry
Indian gooseberry (or amla) is high in vitamin C that helps reduce your body heat. For positive effect, you can use it as follows.
- Mix 4 parts of water with 1 part amla juice. You can add a little sugar or salt to improve the taste. It is suggested to consume it two times daily during the summer in order to prevent heat stress.
- Another option is to add amla juice (2 teaspoons), raw honey (1 teaspoon) and lemon juice (1 teaspoon) to a glass of water. You had better enjoy this every day in the morning on an empty stomach.
Buttermilk
Buttermilk is one of the useful home remedies to reduce body heat, according to Ayurveda. It can also be beneficial for men who have high metabolism and women who suffer from hot flashes. In addition, it also provides your body with the required vitamins and minerals which are lost during excessive sweating.
- Drink buttermilk (a glass) with your breakfast in the summer to maintain your body cool throughout the day.
- Another option is to blend together thick yogurt (½ cup), some water (½ cup) and a pinch of salt. You can drink this homemade buttermilk two times daily.
Poppy Seeds
Poppy seeds (or opium) are very effective in regulating body temperature. For best results, you can mix crushed poppy seeds (1 teaspoon) and a little sugar. It is recommended to consume it once every day during the summer season in order to remove excessive body heat. Another option for home remedies to reduce body heat is to eat poppy seeds (a small amount) before going to bed.
Home Remedies To Reduce Body Heat – Additional Tips
- Avoid exposure to excessive humidity and heat whenever possible.
- Drink fresh pomegranate juice (a glass) mixed with almond oil (a few drops) every morning.
- Wear lightweight, loose-fitting clothing that can help you stay cool.
- Avoid wearing excess clothes that can prevent sweat from evaporating easily.
- Sleep in a well-ventilated, cool area.
- Do not drink alcoholic and caffeinated beverages as they affect your body’s ability to regulate your temperature.
- Drink enough water every day in order to supply fluids lost through sweating.
- Try to stay in air-conditioned or a shady place during peak summer days.
- Do not sit inside a car parked in the sun.
- Stay away from hot and spicy foods as well as fatty and fried foods.
- Do not eat nuts every day as they can increase heat in the body. Try to eat them about 2 or 3 times per week.
Homeopathic remedies for hyperthermia
Homeopathic treatment for the various stages of heat and sun exposure are often helpful in stabilizing an individual and overcoming mild overheating. If an individual is suffering from heat stroke, treat with the appropriate remedy en route to your healthcare practitioner or hospital.
Belladonna – Agonizing, sudden, shooting headache with throbbing making the individual scream in pain. Bright red face dilated pupils, glassy-eyed, fixed stare with no expression, no thirst but has a dry mouth.
Bryonia – Severe headache made worse by the slightest motion. The individual is extremely thirsty for large amounts of cold water.
Aconite – Faint and dizzy with a headache after prolonged, direct exposure to the sun. Individual may say he feels like he is dying, be anxious and restless.
Carbo Veg – Collapse from excess heat with clamminess of the skin and stomach complaints. The individual wants to be fanned and needs to feel moving air.
Glonoinum – First remedy for sunstroke. Agonizing congestive headache after exposure to sun and heat. Hot face and cold extremities, irritability, and confusion. Pounding pain, compare to Belladonna.
Gelsemium – Drowsiness, headache in the back of the head, no thirst, weakness, comatose and useful for sunstroke.
Lachesis – Excellent for treating headaches from sun exposure especially if they are worse on the left side. The individual feels worse after waking from sleep, feels faint and dizzy.
Natrum Carb – Debilitated as a result of heat exposure. Is chronically affected by heat and sunstroke. A headache is worse from the slightest mental effort.
References
























Visitor Rating: 5 Stars
Visitor Rating: 5 Stars